Ear Cancer
Ear Cancer is a rare cancer. Most of these cancers start in the skin of the outer ear.
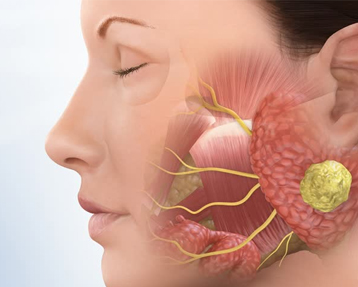
Ear cancer can affect both the inner and external parts of the ear. It often starts as a skin cancer on the outer ear that then spreads throughout the various ear structures, including the ear canal and the eardrum.
It may also start from within the ear. It can affect the bone inside the ear, called the temporal bone. The temporal bone also includes the mastoid bone. This is the bony lump you feel behind your ear.
Symptoms
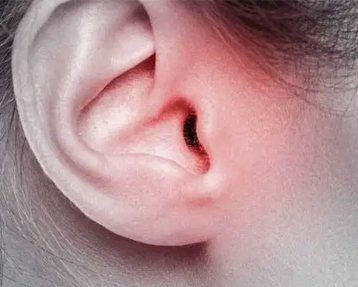
- skin ulcers that bleed
- lump in or near the entrance to the ear canal
- hearing loss
- discharge from the ear
- Dizziness
- Headache
- pearly white lumps under the skin
- scaly patches of skin that remain,even after moisturizing
Types of Ear Cancer
The most common type of ear cancer is squamous cell cancer. Other types of cancer of the ear canal, middle or inner ear include:
- Melanoma Ear Cancer
- Adenoid Cystic Ear Cancer
- Adenocarcinoma Ear Cancer
- Basal cell Ear Cancer
Diagnosis
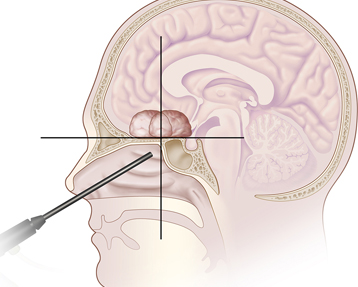
This procedure is called a biopsy. A biopsy may be done under local or general anesthesia (so you don’t feel any pain), depending on the location of the affected area.
Cancerous growths on the inner ear can be more difficult to reach. This makes it harder for your doctor to biopsy without damaging surrounding tissue. Your doctor may have to rely on imaging tests, such as an MRI or CT scan to get an idea if cancer is present.