Parapharyngeal Cancer
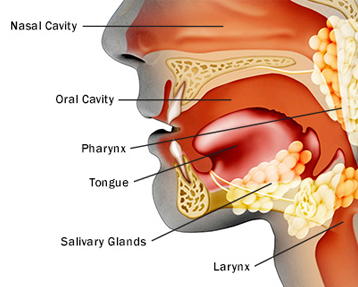
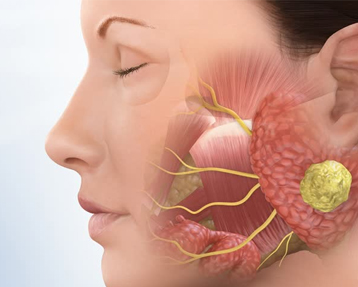
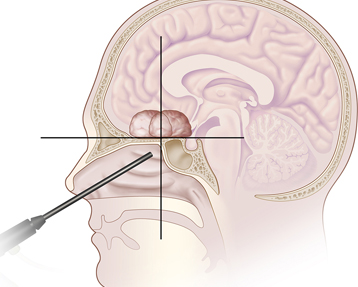
Parapharyngeal cancer is a type of throat cancer that forms in the pharynx, the hollow tube that runs from the back of the nose to the top of the esophagus. The pharynx has three distinct parts: the nasopharynx (upper part), the oropharynx (middle part, including the back of the mouth, base of the tongue, and tonsils), and the hypopharynx (lower part). Cancer can form in the cells of all three areas and has different characteristics depending on its location.
Signs & Symptoms
- Swelling of the neck
- Nasal Congestion (a blocked nose)
- Persistent headaches
- Facial pain
- Nosebleeds
- Changes in hearing
- Ringing in the ears (tinnitus)
- Chronic sore throat
- A lump in the nose or back of the mouth, throat or neck.
- Ear or jaw pain.
- Difficulty breathing
- A change in voice, or unusual hoarseness
- Frequent nose bleeds.
- Headaches
Types of Pharyngeal Cancer
This cancer develops in the pharynx, which is the hollow tube that runs from behind your nose to the top of your windpipe. Pharyngeal cancers that develop in the neck and throat include:
- Nasopharynx cancer (upper part of the throat)
- Oropharynx cancer (middle part of the throat)
- Hypopharynx cancer (bottom part of the throat)
Treatment
Radiation therapy: combined with chemotherapy (chemoradiation) is the most common treatment. In most cases, surgery is only required if the tumor returns after chemoradiation therapy.