Salivary Gland Tumor
Salivary gland cancer is a type of head and neck cancer. It is a rare disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the salivary glands.Being exposed to certain types of radiation may increase the risk of salivary cancer.Signs of salivary gland cancer include a lump or trouble swallowing. The salivary glands make saliva and release it into the mouth. Saliva has enzymes that help digest food and antibodies that help protect against infections of the mouth and throat.
3 Types of Salivary Gland Tumor
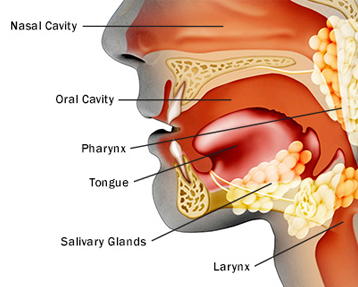
- Parotid glands :These are the largest salivary glands and are found in front of and just below each ear. Most major salivary gland tumors begin in this gland
- Sublingual glands :These glands are found under the tongue in the floor of the mouth.
- Submandibular glands: These glands are found below the jawbone.
Of all the above, PAROTID TUMOR is most common, In fact as many as 80% of salivary gland tumors begin in the parotid glands.
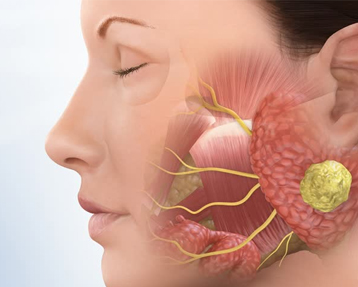
Parotid Tumor
Parotid glands are salivary glands which are situated in the area in front of ear. It produces saliva to keep our mouth wet, if you see or think about delicious food it starts producing saliva and opens in the mouth via a duct, adjacent to upper 2 molar teeth or upper 2nd last tooth.
Parotid gland can get affected by tumors or lump which in 80% times is not cancerous. These Benign parotid tumors tend to grow but do not spread to other parts of the body. As they grow, they may push on the surrounding tissue or wrap around them; if the nerve is immediately next to the tumor then the nerve can in time be either pressed on or engulfed by the salivary gland tumor making surgery more difficult. The most common benign tumor of the parotid gland and the most common of which is Pleomorphic adenoma also called Benign Mixed Tumor. They will usually been seen as swelling which keeps on growing with time slowly and will usually not cause any pain. If there is pain or recently it has rapidly increased in size then we suggests cancerous conversion of the benign tumor.
Diagnosis
To diagnose it one needle test is done called FNAC by which it is confirmed that swelling is cancerous or not cancerous. Surgeon will require CT scan or MRI for looking inside the nature of lump and likely any extension.
Treatment
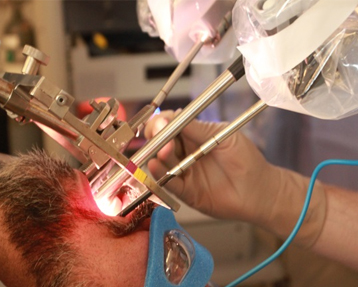
Surgery is challenging as there is nerve called Facial nerve which runs deep to the tumor so this nerve and its branches needs to be preserved. This nerve controls the facial expressions. Its damage during surgery leads to inability to close the eyelid and deviation or mouth to while smiling and in worst cases it may lead to permanent facial paralysis of the patient. In order to avoid this we take utmost care in identifying the facial nerve prior to the removal of Parotid Gland. Surgery is the only successful way by which it can be removed. Surgeon’s experience and use of adjunctive instruments like nerve stimulator to help in identifying the finer branches with large tumours are the key points of successful removal of tumor.
Recovery
Patients are able to go home on same day or day after surgery, depending on the overall health and other parameters. After 1-2 weeks of surgery they are allowed to eat everything but forbidden from taking Pan Masala, Gutka and are also refrained from heavy lifting exercises.